Dental hygiene is a crucial aspect of oral health care. Maintaining good dental hygiene is essential for preventing common dental issues such as cavities, gum disease, and bad breath.
Brushing Techniques:
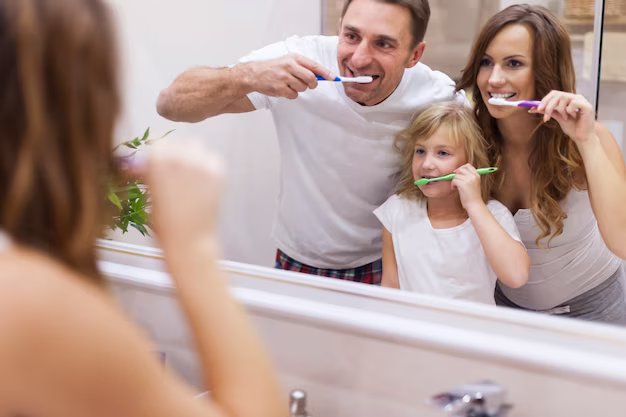

- Choosing the Right Toothbrush: It is important to select a toothbrush with medium to firm bristles that won’t damage the gums or enamel, electric toothbrushes can also be effective and ones that employ sonic movement can be very effective in plaque removal
- Proper Brushing Frequency: It is important to brush at least twice a day, ideally in the morning and before bedtime.
- Toothpaste Selection: There are great benefits of using fluoride toothpaste, which helps strengthen tooth enamel and prevent cavities.
- Brushing Duration: We recommend brushing for a minimum of two minutes to ensure thorough cleaning, we suggest using a timer or listening to a short song to make it fun.
- Brushing Technique: A good brushing technique involves holding the toothbrush at a 45-degree angle to the gums and using gentle circular or back-and-forth motions. Remember to brush all surfaces of their teeth: front, back, and chewing surfaces.
- Tongue and Cheek Cleaning: Gently brush your tongue and the inside of your cheeks to remove bacteria and freshen breath.
- Avoiding Aggressive Brushing: Please be cautious against aggressive brushing, as it can lead to gum recession and enamel erosion, brushing harder doesn’t result in better cleaning and can lead to damage.
- Regular Replacement: Replace toothbrush or toothbrush head every three to four months or sooner if bristles appear frayed.
- Children’s Dental Care: Teaching children proper tooth brushing techniques is essential for their oral health. Start early, introduce tooth brushing as part of your child’s daily routine from a young age, ideally when the first tooth appears, using a soft-bristle infant toothbrush. For children under the age of 3, use a smear of fluoride toothpaste about the size of a grain of rice. For children aged 3-6, a pea-sized amount is appropriate. Children often lack the dexterity to brush effectively on their own until around the age of 6 or 7. Parents should supervise and assist with brushing until then. Teach your child to hold the toothbrush at a 45-degree angle to the gum line. Use gentle, circular motions for about two minutes to clean all tooth surfaces, including the front, back, and chewing surfaces. To encourage compliance, make tooth brushing a fun and engaging activity. Use colourful toothbrushes and toothpaste, and play their favourite songs for the duration of brushing. Emphasize the importance of brushing in the morning and before bedtime to remove food particles and plaque. Consider implementing a reward system, such as a sticker chart, to motivate your child to brush regularly and effectively. Children often learn by example. Brush your teeth alongside them to demonstrate proper technique and the importance of good oral hygiene.
Diet and Oral Health:
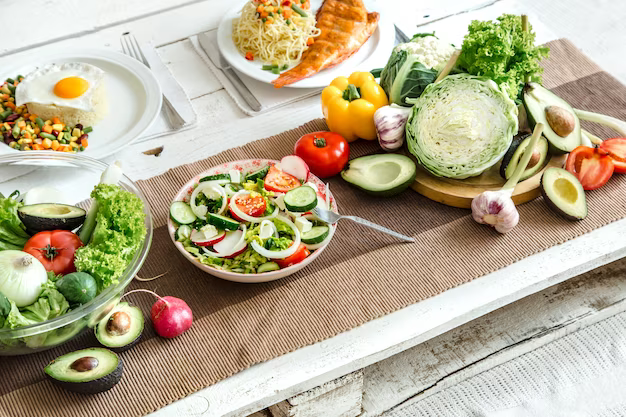

There is an important connection between a good balanced diet, nutrition, and maintaining healthy teeth and gums. It is important to maintaining a diet that supports oral health: Excess sugar promotes tooth decay. Aim to reduce consumption of sugary snacks, sodas, and sweets.
- Water is the best drink for oral health. It helps rinse away food particles and bacteria, and it’s often fortified with fluoride in many areas. Adequate hydration is crucial for saliva production. Dry mouth can increase the risk of cavities, so please drink enough water.
- High-fibre fruits and vegetables, such as carrots, and celery, help stimulate saliva production, which naturally cleanses the mouth and neutralizes acids.
- Dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt are rich in calcium, which strengthens tooth enamel. They also contain casein, a protein that helps prevent tooth decay.
- Consider lean protein sources like poultry, fish, and legumes. These foods provide essential nutrients for gum health and repair.
- Nuts and seeds are excellent sources of minerals like calcium and phosphorus, which contribute to strong teeth and gums.
- Green tea contains compounds that can help reduce oral bacteria and inhibit the growth of harmful microbes, be careful to consume in moderation as it can cause teeth staining
- Acidic foods and beverages, like citrus fruits and vinegar, can erode tooth enamel. Use in moderation and rinse with water after consumption.
- Chewing sugar-free gum after meals can stimulate saliva production, helping to wash away food particles and neutralize acids.
- Frequent snacking, especially on sugary or acidic foods, can lead to continuous acid attacks on teeth. Use structured meal times instead.
- The importance of regular dental check-ups is for the early detection of problems. Dentists can detect and address any oral health issues and provide personalized dietary advice.
 Regular Dental Check-ups:
Regular Dental Check-ups:
We stress the importance of routine dental check-ups and cleanings for early detection of issues.
Common Dental Problems:
Tooth sensitivity can be triggered by various factors, including tooth decay, gum recession, enamel erosion, or teeth grinding. The first step is to identify the root cause by visiting a dentist for a thorough examination. Desensitizing toothpaste containing ingredients like potassium nitrate or strontium chloride can be very helpful. These toothpaste types help block nerve signals that cause sensitivity. Acidic foods and beverages can weaken tooth enamel. Reducing the consumption of acidic items like citrus fruits, sodas, and vinegar-containing foods will help. A tooth-friendly diet rich in calcium and phosphates, which help strengthen enamel will also help. Dairy products, leafy greens, and nuts are good choices. There is great importance for regular dental check-ups. Your dentist can identify and treat dental issues that may be causing sensitivity and the dentist can provide personalized advice.
Flossing Techniques:
Begin by choosing dental floss that suits your preferences and dental needs. Options include waxed, un-waxed, flavoured, and dental tape. Find what works best for you or ask your dentist for suggestions suitable for you. Cut a piece of dental floss about 18 inches long (45 cm). This provides enough length to use a clean section between each tooth. Wind the ends of the floss around your fingers, leaving about 1-2 inches (2-5 cm) of floss to work with. Hold the floss taut between your thumb and forefingers. Insert the floss gently between two teeth using a sawing motion. Be careful not to snap or force it, as this can harm your gums. Once the floss is between the teeth, curve it into a “C” shape against one tooth. Glide it up and down while gently hugging the tooth’s surface. Repeat this motion for both sides of the tooth, including just under the gum-line. After cleaning one tooth, unwind a bit of clean floss from one finger while winding the used floss onto the other. This ensures you’re using a fresh section for each tooth. Move from tooth to tooth, ensuring you floss both sides of each tooth in the same manner. Don’t forget to floss the back molars, which can be easily overlooked. Be gentle when flossing to avoid injuring your gums. If you’re new to flossing, you may experience some bleeding initially, but this should improve with consistent flossing. After flossing, rinse your mouth with water to remove dislodged debris and then pat your teeth dry with a clean tissue or cloth. Floss at least once a day, ideally before bedtime, to remove dislodged particles and prevent plaque build-up. By following these steps, you can maintain healthy teeth and gums.

To book a check-up, please call:
Notting Hill Branch – 020 7229 4813
Shepherds Bush Branch – 020 8743 4065
Heston Branch – 020 8570 0435

